How to use the Nutrition Program to test a healthy meal for a 4 year old.
- Choose your menu – mine is going to be Chilli con carne (mild), Boiled rice, broccoli, with plain yogurt and Fruit compote.

Put the recipes into My Recipes in Nutrition Program – Chilli con carne and Fruit compote
 This shows the simple Fruit compote ingredients.
This shows the simple Fruit compote ingredients.
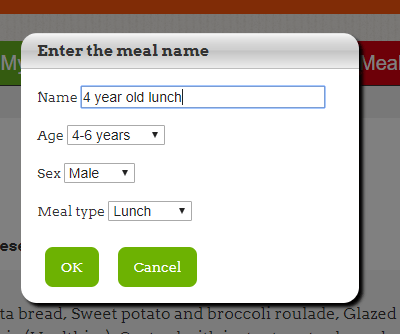
3. Go to My Meals and Enter the meal name – my example Name 4 year old lunch, Choose the Age 4-6 years, Sex – male or female, Meal type Lunch
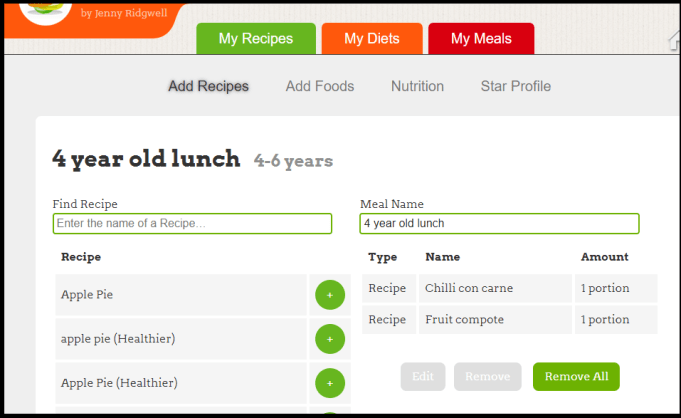
Add Recipes to the lunch – in this case, Chilli con carne and Fruit compote – the ones you have made. It adds 1 portion.
4. Now Add Foods – these are foods on the database that are already cooked. In this example I am adding a portion of rice, white, boiled, then broccoli boiled in unsalted water, then yogurt, fat free, natural.
5. The meal is now complete so look at  Nutrition. The Program analyses the meal for a 4-6 year old and shows you the % of Recommended Meal Intake.
Nutrition. The Program analyses the meal for a 4-6 year old and shows you the % of Recommended Meal Intake.
You can see that the meal is 143% of what is needed for 4-6 year old so I need to cut down the portion size of the recipe.
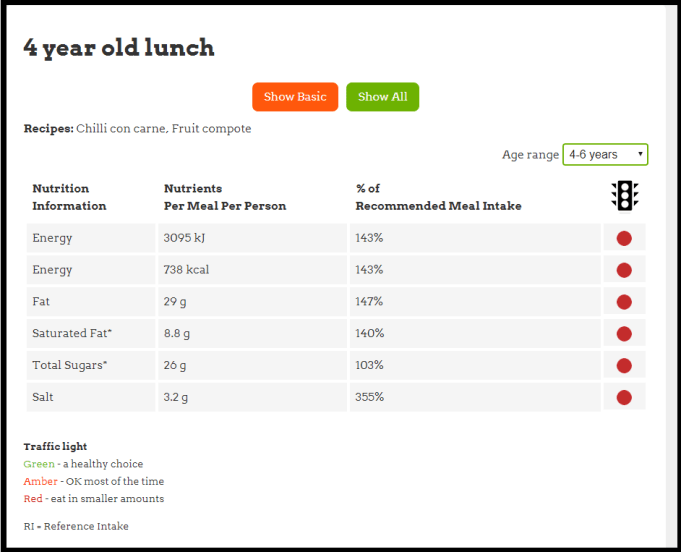
The Traffic lights are showing red and Salt shows 355% which is much too high. So lots of work to be done!